本篇记录了leetcode的hot100的解题思路。
哈希 字母异位词 给你一个字符串数组,请你将 字母异位词 组合在一起。可以按任意顺序返回结果列表。
字母异位词 是由重新排列源单词的所有字母得到的一个新单词。
示例 1:
1 2 输入: strs = ["eat", "tea", "tan", "ate", "nat", "bat"] 输出: [["bat"],["nat","tan"],["ate","eat","tea"]]
思路:遍历每一个字符串,对其排序得到newstr,利用一个hashmap,key为排序后的字符串newstr,value为排序为newstr的字符串,如果map里面没有newstr,则创建一个list并添加当前遍历的字符串,如果已经有了newstr,则将当前遍历的字符串加入进去。遍历完后map里面的key就是答案。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams (String[] strs) { List<List<String>> res=new ArrayList <>(); Map<String,List<String>> map=new HashMap <>(); for (String s:strs){ char str[]=s.toCharArray(); Arrays.sort(str); String newstr=new String (str); if (map.containsKey(newstr)){ map.get(newstr).add(s); }else { List<String> a=new ArrayList <>(); a.add(s); map.put(newstr,a); } } for (Map.Entry<String,List<String>> entry:map.entrySet()){ res.add(entry.getValue()); } return res; } }
最长连续序列 给定一个未排序的整数数组 nums ,找出数字连续的最长序列(不要求序列元素在原数组中连续)的长度。
请你设计并实现时间复杂度为 O(n) 的算法解决此问题。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:nums = [100,4,200,1,3,2] 输出:4 解释:最长数字连续序列是 [1, 2, 3, 4]。它的长度为 4。
思路:先利用set去重。遍历set,找到起始元素,如果遍历到num,且存在num-1。则num不是起始元素。找到起始元素后以此判断num+1是否存在,如果存在,更新最长长度。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public int longestConsecutive (int [] nums) { Set<Integer> set=new HashSet <>(); for (int num:nums){ set.add(num); } int max=0 ; for (int num:set){ if (set.contains(num-1 )){ continue ; } int cur=1 ; int data=num; while (set.contains(data+1 )){ cur++; data++; } max=Math.max(cur,max); } return max; } }
双指针 移动零 给定一个数组 nums,编写一个函数将所有 0 移动到数组的末尾,同时保持非零元素的相对顺序。
请注意 ,必须在不复制数组的情况下原地对数组进行操作。
示例 1:
1 2 输入: nums = [0,1,0,3,12] 输出: [1,3,12,0,0]
思路:看似移动0,实则移动非0。两个指针i,j。i再左边占着非0元素的坑,j在右边找0元素。找到了就交换,交换后i所占的坑就不是非0元素的坑了,则需要++;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public void moveZeroes (int [] nums) { int i = 0 , j = 0 ; while (j < nums.length) { if (nums[j] != 0 ) { int temp = nums[i]; nums[i] = nums[j]; nums[j] = temp; i++; } j++; } } }
三数之和 给你一个整数数组 nums ,判断是否存在三元组 [nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]] 满足 i != j、i != k 且 j != k ,同时还满足 nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0 。请你返回所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。
注意: 答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
示例 1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 输入:nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4] 输出:[[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]] 解释: nums[0] + nums[1] + nums[2] = (-1) + 0 + 1 = 0 。 nums[1] + nums[2] + nums[4] = 0 + 1 + (-1) = 0 。 nums[0] + nums[3] + nums[4] = (-1) + 2 + (-1) = 0 。 不同的三元组是 [-1,0,1] 和 [-1,-1,2] 。 注意,输出的顺序和三元组的顺序并不重要。
思路:固定一个数,变成两数之和。先对数组排序。定义i,left,right。对应first,second,third。等价于0-first=second+third。
定义target=0-first,如果target<second+third,说明second+third要减小,则right–。如果target>second+third,说明second+third要增大,则left++。如果target=second+third,则找到了这样的三元组,找到之后,如果left前面后right后面又重复的元素,则要进行去重。第一轮结束后,第二轮开始就要判断first是否重复,也要进行去重。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> threeSum (int [] nums) { List<List<Integer>> res=new ArrayList <>(); Arrays.sort(nums); for (int i=0 ;i<nums.length-2 ;i++){ int first=nums[i]; if (first>0 ){ break ; } if (i>0 &&nums[i]==nums[i-1 ]){ continue ; } int left=i+1 ; int right=nums.length-1 ; while (left<right){ int target=0 -first; int second=nums[left]; int third=nums[right]; if (target<second+third){ right--; }else if (target>second+third){ left++; }else { List<Integer> list=new ArrayList <>(); Collections.addAll(list,first,second,third); res.add(list); while (left<right&&nums[left]==nums[left+1 ]){ left++; } left++; while (left<right&&nums[right]==nums[right-1 ]){ right--; } right--; } } } return res; } }
接雨水 给定 n 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 输出:6 解释:上面是由数组 [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 表示的高度图,在这种情况下,可以接 6 个单位的雨水(蓝色部分表示雨水)。
思路:填坑法:如果下一场大雨,这些柱子被填满后最高的柱子往两侧都是单调的,左侧是递增,右侧是递减,那么为什么可以依据这个规则求出填满后的状态,然后减去初始状态就是答案。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution { public int trap (int [] height) { int max=0 ,index=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<height.length;i++){ if (height[i]>max){ max=height[i]; index=i; } } int res=0 ; for (int i=1 ;i<index;i++){ if (height[i]<height[i-1 ]){ res=res+height[i-1 ]-height[i]; height[i]=height[i-1 ]; } } for (int i=height.length-2 ;i>index;i--){ if (height[i]<height[i+1 ]){ res=res+height[i+1 ]-height[i]; height[i]=height[i+1 ]; } } return res; } }
滑动窗口 无重复字符的最长子串 给定一个字符串 s ,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的 最长 子串 的长度。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入: s = "abcabcbb" 输出: 3 解释: 因为无重复字符的最长子串是 "abc",所以其长度为 3。
思路:滑动窗口通式:
定义窗口状态为无重复字符,用一个map来记录字符个数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int lengthOfLongestSubstring (String s) { int map[] = new int [200 ]; char str[] = s.toCharArray(); int res = 0 ; for (int left = 0 , right = 0 ; right < s.length(); right++) { map[str[right]]++; while (map[str[right]] > 1 ) { map[str[left]]--; left++; } res = Math.max(res, right - left + 1 ); } return res; } }
找到字符串中所有字母异位词 给定两个字符串 s 和 p,找到 s 中所有 p 的 异位词 的子串,返回这些子串的起始索引。不考虑答案输出的顺序。
示例 1:
1 2 3 4 5 输入: s = "cbaebabacd", p = "abc" 输出: [0,6] 解释: 起始索引等于 0 的子串是 "cba", 它是 "abc" 的异位词。 起始索引等于 6 的子串是 "bac", 它是 "abc" 的异位词。
思路:小技巧:将map初始化为p的字符数量,加入窗口时做的是–,当遇到不是p中的字符数,会变成负数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public List<Integer> findAnagrams (String s, String p) { int map[] = new int [300 ]; char str[] = s.toCharArray(); for (Character ch : p.toCharArray()) { map[ch]++; } List<Integer> res = new ArrayList <>(); for (int left = 0 , right = 0 ; right < s.length(); right++) { map[str[right]]--; while (map[str[right]] < 0 ) { map[str[left]]++; left++; } if (right - left + 1 == p.length()) { res.add(left); } } return res; } }
最小覆盖子串 给你一个字符串 s 、一个字符串 t 。返回 s 中涵盖 t 所有字符的最小子串。如果 s 中不存在涵盖 t 所有字符的子串,则返回空字符串 "" 。
注意:
对于 t 中重复字符,我们寻找的子字符串中该字符数量必须不少于 t 中该字符数量。
如果 s 中存在这样的子串,我们保证它是唯一的答案。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:s = "ADOBECODEBANC", t = "ABC" 输出:"BANC" 解释:最小覆盖子串 "BANC" 包含来自字符串 t 的 'A'、'B' 和 'C'。
思路:直接看代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution { public String minWindow (String s, String t) { char str[] = s.toCharArray(); int map[] = new int [300 ]; for (char ch : t.toCharArray()) { map[ch]++; } int resleft = 0 , resright = s.length(); int count = 0 ; for (int left = 0 , right = 0 ; right < s.length(); right++) { map[str[right]]--; if (map[str[right]] >= 0 ) { count++; } while (count == t.length()) { if (resright - resleft > right - left) { resleft = left; resright = right; } if (map[str[left]] >= 0 ) { count--; } map[str[left]]++; left++; } } return resright == str.length ? "" : s.substring(resleft, resright + 1 ); } }
子串 和为 K 的子数组 给你一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数 k ,请你统计并返回 该数组中和为 k 的子数组的个数 。
子数组是数组中元素的连续非空序列。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:nums = [1,1,1], k = 2 输出:2
思路:求子数组的和,首先想到前缀和,等价与求prefix[j]-prefix[i-1]=k ==> prefix[j]-k=prefix[i-1]==》两数之和
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public int subarraySum (int [] nums, int k) { int n = nums.length; int prefixSum[] = new int [n]; int sum = 0 ; int count = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { sum = sum + nums[i]; prefixSum[i] = sum; } Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); map.put(0 , 1 ); for (int num : prefixSum) { if (map.containsKey(num - k)) { count = count + map.get(num - k); } map.put(num, map.getOrDefault(num, 0 ) + 1 ); } return count; } }
滑动窗口最大值 给你一个整数数组 nums,有一个大小为 k 的滑动窗口从数组的最左侧移动到数组的最右侧。你只可以看到在滑动窗口内的 k 个数字。滑动窗口每次只向右移动一位。
返回 滑动窗口中的最大值 。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], k = 3 输出:[3,3,5,5,6,7]
思路:维护一个双端队列,且要是从左(尾)到右(头)是单调的。看代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public int [] maxSlidingWindow(int [] nums, int k) { int n = nums.length; int res[] = new int [n - k + 1 ]; Deque<Integer> q = new ArrayDeque <>(); int index = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { while (!q.isEmpty() && q.peekFirst() < i - k + 1 ) { q.pollFirst(); } while (!q.isEmpty() && nums[i] > nums[q.peekLast()]) { q.pollLast(); } q.addLast(i); if (i - k + 1 >= 0 ) { res[index++] = nums[q.peekFirst()]; } } return res; } }
普通数组 最大子数组和 给你一个整数数组 nums ,请你找出一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。
子数组 是数组中的一个连续部分。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4] 输出:6 解释:连续子数组 [4,-1,2,1] 的和最大,为 6 。
思路1:前缀和,题目求nums[i,j]的最大值,等价于求prefixSum[j]-prefixSum[i-1]的最大值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int maxSubArray (int [] nums) { int prefixSum[] = new int [nums.length]; prefixSum[0 ] = nums[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++) { prefixSum[i] = prefixSum[i - 1 ] + nums[i]; } int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE; int min = 0 ; for (int num : prefixSum) { max = Math.max(max, num - min); min = Math.min(min, num); } return max; } }
思路2:动态规划:dp[i]表示以nums[i]结尾的连续子数组最大和。
1 2 3 转移方程:dp[i]=nums[i]+max(d[i-1],0) 如果dp[i-1]是负数,则是负优化,舍弃。 如果dp[i-1]是正数,则是正优化,加上。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int maxSubArray (int [] nums) { int dp[]=new int [nums.length]; dp[0 ]=nums[0 ]; int max=dp[0 ]; for (int i=1 ;i<nums.length;i++){ dp[i]=nums[i]+Math.max(0 ,dp[i-1 ]); max=Math.max(max,dp[i]); } return max; } }
空间优化:dp[i]只依赖于dp[i-1],所以可以不用数组,用一个变量premax=nums[i]+Math.max(0,premax);右侧的premax就是先前的值,左侧的premax就是等待更新的值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int maxSubArray (int [] nums) { int max = nums[0 ]; int premax = nums[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++) { premax = nums[i] + Math.max(0 , premax); max = Math.max(max, premax); } return max; } }
合并区间 以数组 intervals 表示若干个区间的集合,其中单个区间为 intervals[i] = [starti, endi] 。请你合并所有重叠的区间,并返回 一个不重叠的区间数组,该数组需恰好覆盖输入中的所有区间 。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:intervals = [[1,3],[2,6],[8,10],[15,18]] 输出:[[1,6],[8,10],[15,18]] 解释:区间 [1,3] 和 [2,6] 重叠, 将它们合并为 [1,6].
思路:先对数组排序,排序规则为按照第一个元素排序。排序之后把第一个元素加入到一个集合里,然后遍历后面的数组,如果集合的最后一个 数组的[1]>=当前遍历数组的[0],说明这两个数组可以合并,集合的最后一个 数组的[1]=这两个数组的[1]的最大值。如果不能合并就直接加入到集合里,最后把集合转成数组。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public int [][] merge(int [][] intervals) { Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> a[0 ] - b[0 ]); List<int []> res = new ArrayList <>(); res.add(intervals[0 ]); for (int i = 1 ; i < intervals.length; i++) { int listEnd[] = res.get(res.size() - 1 ); int interval[] = intervals[i]; if (listEnd[1 ] >= interval[0 ]) { listEnd[1 ] = Math.max(listEnd[1 ], interval[1 ]); } else { res.add(interval); } } return res.toArray(new int [res.size()][2 ]); } }
轮转数组 给定一个整数数组 nums,将数组中的元素向右轮转 k 个位置,其中 k 是非负数。
示例 1:
1 2 输入: nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], k = 3 输出: [5,6,7,1,2,3,4]
思路1:先将整个数组翻转,再翻转0到k-1,再翻转k到n-1;注意k>n的的话要取余。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public void rotate (int [] nums, int k) { int n = nums.length; reverse(nums, 0 , n - 1 ); reverse(nums, 0 , k % n - 1 ); reverse(nums, k % n, n - 1 ); } public void reverse (int nums[], int i, int j) { while (i < j) { swap(nums, i, j); i++; j--; } } public void swap (int nums[], int i, int j) { int temp = nums[j]; nums[j] = nums[i]; nums[i] = temp; } }
思路2:原地打转(环形替换):将数组看成一个环,每一个元素都有一个目标值,环上的元素依次向右移动,直到回到原点。
用cur记录当前位置(最开始是start=0),pre保存当前位置的值,计算出下一个位置的值nextIndex,把下一个位置的值先保存在temp中,再替换成pre,然后cur移动到nextIndex重复下一次,没移动一次就技术一次,每个元素都操作完成后就结束循环。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public void rotate (int [] nums, int k) { int n = nums.length; k = k % n; int count = 0 ; int start = 0 ; while (count < n) { int cur = start; int pre = nums[cur]; do { int nextIndex = (cur + k) % n; int temp = nums[nextIndex]; nums[nextIndex] = pre; pre = temp; cur = nextIndex; count++; } while (cur != start); start++; } } }
除自身以外数组的乘积 给你一个整数数组 nums,返回 数组 answer ,其中 answer[i] 等于 nums 中除 nums[i] 之外其余各元素的乘积 。
题目数据 保证 数组 nums之中任意元素的全部前缀元素和后缀的乘积都在 32 位 整数范围内。
请 不要使用除法, 且在 O(n) 时间复杂度内完成此题。
示例 1:
1 2 输入: nums = [1,2,3,4] 输出: [24,12,8,6]
思路1:空间优化:不用额外定义两个数组,第一次遍历后顺便求出前缀乘积,第二次遍历顺便求出后缀乘积。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public int [] productExceptSelf(int [] nums) { int res[] = new int [nums.length]; for (int i = 0 ; i < res.length; i++) { res[i] = 1 ; } int left = 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++) { res[i] *= left; left *= nums[i]; } int right = 1 ; for (int j = nums.length - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j--) { res[j] *= right; right *= nums[j]; } return res; } }
缺失的第一个正数 给你一个未排序的整数数组 nums ,请你找出其中没有出现的最小的正整数。
请你实现时间复杂度为 O(n) 并且只使用常数级别额外空间的解决方案。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:nums = [3,4,-1,1] 输出:2 解释:1 在数组中,但 2 没有。
思路:原地哈希。既然是找最小的正整数,所以我们只关心[1,n]。对于理想情况下标0处的位置是1,下标1处的位置是2。。。。。。
所以遍历数组时候,我们把当前处于[1,n]内的元素放在他理想情况的位置,其他的不管。这样处理后得到的数组就会是1,2,。。。。这样的,我们按顺序遍历,当出现顺序不对的时候,说明缺失的最小的正整数就是他。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution { public int firstMissingPositive (int [] nums) { int n = nums.length; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if (nums[i] < 1 || nums[i] > n) { continue ; } if (nums[i] != nums[nums[i] - 1 ]) { swap(nums,i,nums[i]-1 ); i--; } } for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if (nums[i] != i + 1 ) { return i + 1 ; } } return n + 1 ; } public static void swap (int [] a, int i, int j) { int temp = a[i]; a[i] = a[j]; a[j] = temp; } }
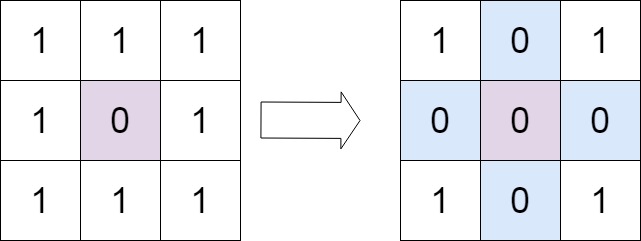
矩阵 矩阵置零 给定一个 *m* x *n* 的矩阵,如果一个元素为 0 ,则将其所在行和列的所有元素都设为 0 。请使用 原地 。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:matrix = [[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[1,1,1]] 输出:[[1,0,1],[0,0,0],[1,0,1]]
思路1:用两个行列数组来标记哪一行哪一列有0:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public void setZeroes (int [][] matrix) { int m = matrix.length; int n = matrix[0 ].length; int hang[] = new int [matrix.length]; int lie[] = new int [matrix[0 ].length]; for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { if (matrix[i][j] == 0 ) { hang[i] = 1 ; lie[j] = 1 ; } } } for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { if (hang[i] == 1 ) { matrix[i][j] = 0 ; } if (lie[j] == 1 ) { matrix[i][j] = 0 ; } } } } }
空间优化:不用额外数组,直接利用第一行和第一列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 class Solution { public void setZeroes (int [][] matrix) { boolean hang=false ; boolean lie=false ; int m=matrix.length,n=matrix[0 ].length; for (int i=0 ;i<m;i++){ if (matrix[i][0 ]==0 ){ lie=true ; break ; } } for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++){ if (matrix[0 ][i]==0 ){ hang=true ; break ; } } for (int i=1 ;i<m;i++){ for (int j=1 ;j<n;j++){ if (matrix[i][j]==0 ){ matrix[0 ][j]=0 ; matrix[i][0 ]=0 ; } } } for (int i=1 ;i<m;i++){ if (matrix[i][0 ]==0 ){ for (int j=0 ;j<n;j++){ matrix[i][j]=0 ; } } } for (int i=1 ;i<n;i++){ if (matrix[0 ][i]==0 ){ for (int j=0 ;j<m;j++){ matrix[j][i]=0 ; } } } if (hang){ for (int i=0 ;i<n;i++){ matrix[0 ][i]=0 ; } } if (lie){ for (int i=0 ;i<m;i++){ matrix[i][0 ]=0 ; } } } }
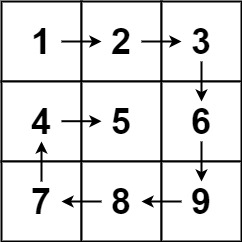
螺旋矩阵 给你一个 m 行 n 列的矩阵 matrix ,请按照 顺时针螺旋顺序 ,返回矩阵中的所有元素。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] 输出:[1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]
思路:从上->右->下->左遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution { public List<Integer> spiralOrder (int [][] matrix) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList <>(); int left = 0 , top = 0 , right = matrix[0 ].length - 1 , down = matrix.length - 1 ; while (left <= right && top <= down) { for (int i = left; i <= right; i++) { res.add(matrix[top][i]); } top++; for (int i = top; i <= down; i++) { res.add(matrix[i][right]); } right--; if (top <= down) { for (int i = right; i >= left; i--) { res.add(matrix[down][i]); } down--; } if (left <= right) { for (int i = down; i >= top; i--) { res.add(matrix[i][left]); } left++; } } return res; } }
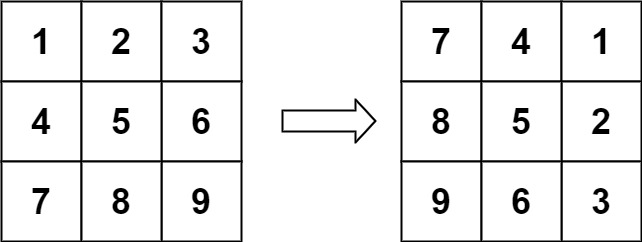
旋转图像 给定一个 n × n 的二维矩阵 matrix 表示一个图像。请你将图像顺时针旋转 90 度。
你必须在** 原地 ** 旋转图像,这意味着你需要直接修改输入的二维矩阵。请不要 使用另一个矩阵来旋转图像。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] 输出:[[7,4,1],[8,5,2],[9,6,3]]
思路1:先对角线翻转再垂直翻转,或者先水平翻转再对角线翻转;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public void rotate (int [][] matrix) { int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0 ].length; int left = 0 , right = n - 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { for (int j = i; j < n; j++) { int temp = matrix[i][j]; matrix[i][j] = matrix[j][i]; matrix[j][i] = temp; } } while (left < right) { for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { int temp = matrix[i][left]; matrix[i][left] = matrix[i][right]; matrix[i][right] = temp; } left++; right--; } } }
思路2:缩圈法:看代码推导
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public void rotate (int [][] matrix) { int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0 ].length; for (int i = 0 ; i < m / 2 ; i++) { for (int j = i; j < n - 1 - i; j++) { int temp = matrix[i][j]; matrix[i][j] = matrix[n - 1 - j][i]; matrix[n - 1 - j][i] = matrix[n - 1 - i][n - 1 - j]; matrix[n - 1 - i][n - 1 - j] = matrix[j][n - 1 - i]; matrix[j][n - 1 - i] = temp; } } } }
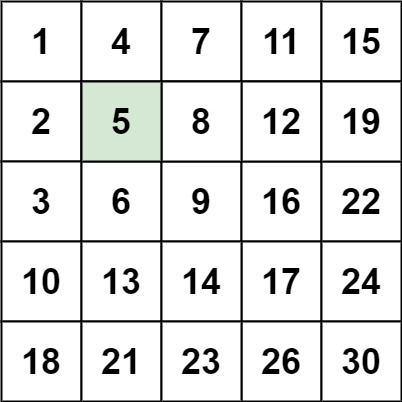
搜索二维矩阵 II 编写一个高效的算法来搜索 *m* x *n* 矩阵 matrix 中的一个目标值 target 。该矩阵具有以下特性:
每行的元素从左到右升序排列。
每列的元素从上到下升序排列。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:matrix = [[1,4,7,11,15],[2,5,8,12,19],[3,6,9,16,22],[10,13,14,17,24],[18,21,23,26,30]], target = 5 输出:true
思路: //观察到右上角元素是这一行的最大值,是这一列的最小值。利用这个思想来进行伪二分
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public boolean searchMatrix (int [][] matrix, int target) { int m = matrix.length; int n = matrix[0 ].length; int right = n - 1 ; int top = 0 ; while (right >= 0 && top <= m - 1 ) { if (matrix[top][right] == target) { return true ; } else if (matrix[top][right] > target) { right--; } else { top++; } } return false ; } }
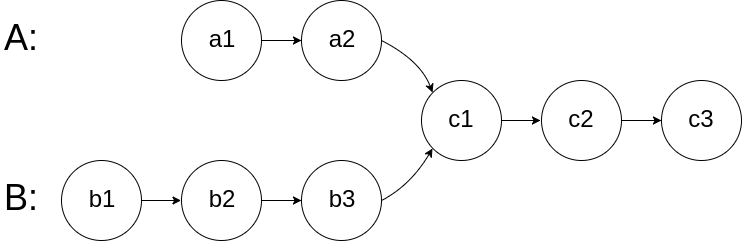
链表 相交链表 给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回 null 。
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交:
题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
思路1:计算两个链表长度,让长的链表走差值。
思路2:用一个集合存储其中一个链表的路径,走第二个链表时判断当前节点是否在集合中。
思路3:走你走过的路:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 struct ListNode* getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode* headA, struct ListNode* headB) { struct ListNode* A = headA; struct ListNode* B = headB; while (A != B) { A = A ? A->next : headB; B = B ? B->next : headA; } return A; }
反转链表 给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5] 输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
思路:没什么好说的:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) { struct ListNode* dum = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); struct ListNode* p = head; dum->next = NULL; while (p) { struct ListNode* q = p->next; p->next = dum->next; dum->next = p; p = q; } return dum->next; }
回文链表 给你一个单链表的头节点 head ,请你判断该链表是否为回文链表。如果是,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:head = [1,2,2,1] 输出:true
思路:用快慢指针找到中间节点,把中间节点后面翻转,然后对比。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 struct ListNode* reverse(struct ListNode* head) { struct ListNode* dum = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); dum->next = NULL; struct ListNode* p = head; while (p) { struct ListNode* q = p->next; p->next = dum->next; dum->next = p; p = q; } return dum->next; } bool isPalindrome (struct ListNode* head) { struct ListNode* slow = head; struct ListNode* fast = head; while (fast->next && fast->next->next) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; } struct ListNode* re = reverse(slow->next); slow->next = re; struct ListNode* p = slow->next; while (p) { if (p->val != head->val) { return false ; } p = p->next; head = head->next; } return true ; }
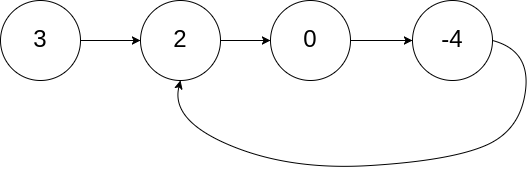
环形链表 给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递 。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环 ,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 输出:true 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
思路:快慢指针:龟兔一直赛跑,兔子总是能追上龟:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 bool hasCycle (struct ListNode* head) { if (head == NULL) { return false ; } struct ListNode* slow = head; struct ListNode* fast = head; while (fast->next && fast->next->next) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; if (slow == fast) { return true ; } } return false ; }
环形链表 II 给定一个链表的头节点 head ,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始 )。如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递 ,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
不允许修改 链表。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点 解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
思路:
当 n=1 时(快指针恰好比慢指针多走一圈):此时a=c,即:头节点到环入口的距离 = 相遇点到环入口的距离
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 struct ListNode* detectCycle(struct ListNode* head) { if (!head) return NULL; struct ListNode* slow = head; struct ListNode* fast = head; while (fast->next && fast->next->next) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; if (slow == fast) { while (slow != head) { slow = slow->next; head = head->next; } return slow; } } return NULL; }
合并两个有序链表 将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4] 输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
思路:没什么好说的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) { struct ListNode* head = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); head->next = NULL; struct ListNode* p = head; while (list1 && list2) { if (list1->val < list2->val) { p->next = list1; list1 = list1->next; } else { p->next = list2; list2 = list2->next; } p = p->next; } p->next = list1 ? list1 : list2; return head->next; }
两数相加 给你两个 非空 的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4] 输出:[7,0,8] 解释:342 + 465 = 807.
思路:就是一个模拟十进制进位的过程,没什么好说的,提前把进位设置为0:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 struct ListNode* addTwoNumbers(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2) { struct ListNode* p = l1; struct ListNode* q = l2; struct ListNode* head = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); head->next = NULL; struct ListNode* r = head; int jin = 0 ; while (p || q) { int a = p ? p->val : 0 ; int b = q ? q->val : 0 ; int sum = (a + b + jin); int res = sum % 10 ; jin = sum / 10 ; struct ListNode* node = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); node->val = res; node->next = r->next; r->next = node; r = node; if (p) p = p->next; if (q) q = q->next; } if (jin == 1 ) { struct ListNode* node = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); node->val = 1 ; node->next = r->next; r->next = node; r = node; } return head->next; }
删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点 给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2 输出:[1,2,3,5]
思路:先让一个指针p走n次,然后再让另一个指针first和p同步走,当p走到尾节点时,first的下一个节点就是要删除的;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 struct ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(struct ListNode* head, int n) { struct ListNode* dum = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); dum->next = head; struct ListNode* p = dum; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { p = p->next; } struct ListNode* first = dum; while (p->next) { p = p->next; first = first->next; } first->next = first->next->next; return dum->next; }
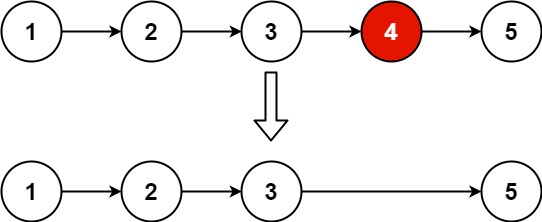
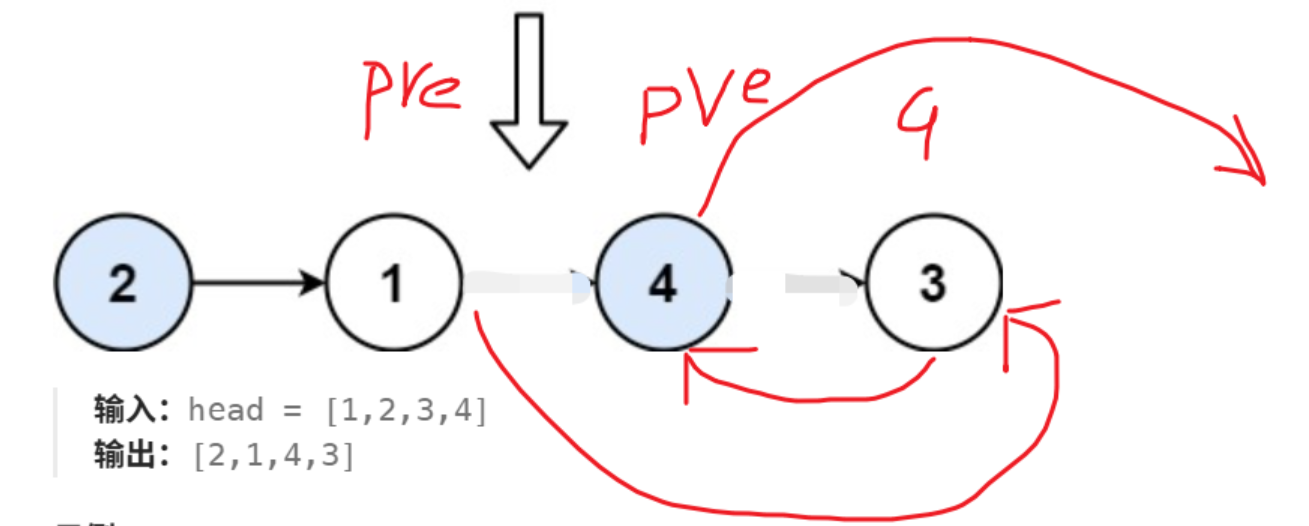
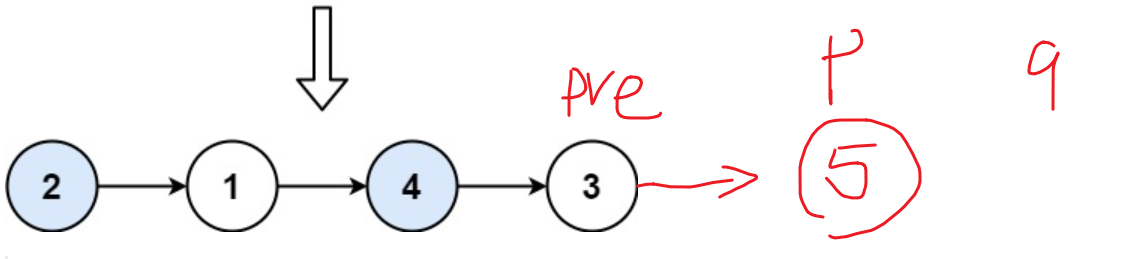
两两交换链表中的节点 给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:head = [1,2,3,4] 输出:[2,1,4,3]
思路:理想情况是两两交换,看图:
两两成对时,最后p为空;结束循环。
有一个单独节点时,p存在、q为空,其实就不同调整,也就是不管了,直接结束循环。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 struct ListNode* swapPairs(struct ListNode* head) { if (!head) return head; if (head->next == NULL) { return head; } struct ListNode* dum = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); dum->next = head; struct ListNode* pre = dum; struct ListNode* p = pre->next; struct ListNode* q = pre->next->next; while (p && q) { p->next = q->next; q->next = pre->next; pre->next = q; pre = q->next; p = pre->next; if (p) q = p->next; } return dum->next; }
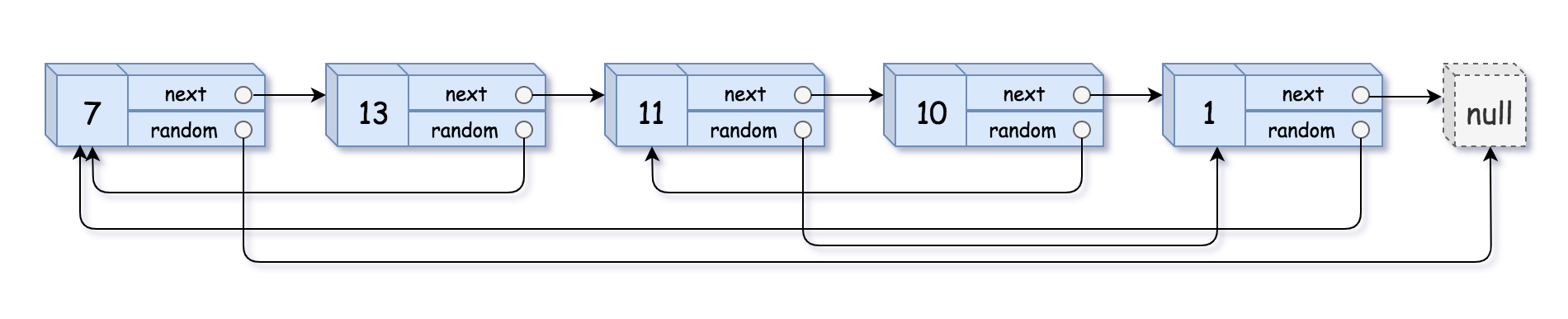
随机链表的复制 给你一个长度为 n 的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针 random ,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
构造这个链表的 深拷贝 。 深拷贝应该正好由 n 个 全新 节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的 next 指针和 random 指针也都应指向复制链表中的新节点,并使原链表和复制链表中的这些指针能够表示相同的链表状态。 复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点
例如,如果原链表中有 X 和 Y 两个节点,其中 X.random --> Y 。那么在复制链表中对应的两个节点 x 和 y ,同样有 x.random --> y 。
返回复制链表的头节点。
用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val, random_index] 表示:
val:一个表示 Node.val 的整数。random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从 0 到 n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为 null 。
你的代码 只 接受原链表的头节点 head 作为传入参数。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]] 输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
思路:特别恶心的一道题,编译器不告诉你哪里空指针。填充链表。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) { struct Node* dum = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); dum->next = head; struct Node* p = dum->next; while (p) { struct Node* node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); node->random = NULL; node->val = p->val; node->next = p->next; p->next = node; p = node->next; } p = dum->next; while (p) { if (p->random != NULL) { p->next->random = p->random->next; } p = p->next->next; } struct Node* s = dum; while (s && s->next) { s->next = s->next->next; s = s->next; } return dum->next; }
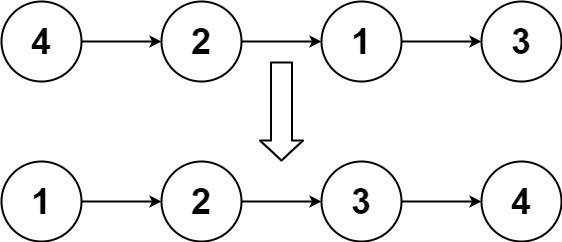
排序链表 给你链表的头结点 head ,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:head = [4,2,1,3] 输出:[1,2,3,4]
思路:细节点:空指针的判断,可以一个一个试
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 struct ListNode* merge(struct ListNode* pre, struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2); struct ListNode* sortList(struct ListNode* head) { struct ListNode* dum = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); dum->next = head; struct ListNode* p = head; int length = 0 ; while (p) { length++; p = p->next; } for (int len = 1 ; len < length; len = len * 2 ) { struct ListNode* pre = dum; struct ListNode* cur = dum->next; while (cur) { struct ListNode* left = cur; for (int i = 1 ; i < len && cur->next; i++) { cur = cur->next; } struct ListNode* right = cur->next; cur->next = NULL; cur = right; for (int i = 1 ; i < len && cur && cur->next; i++) { cur = cur->next; } struct ListNode* next = NULL; if (cur) { next = cur->next; cur->next = NULL; } pre = merge(pre, left, right); cur = next; } } return dum->next; } struct ListNode* merge(struct ListNode* pre, struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2) { while (l1 && l2) { if (l1->val < l2->val) { pre->next = l1; l1 = l1->next; } else { pre->next = l2; l2 = l2->next; } pre = pre->next; } pre->next = l1 ? l1 : l2; while (pre->next) { pre = pre->next; } return pre; }
合并 K 个升序链表 给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]] 输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]
思路1:采用归并排序的思想:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 struct ListNode* merge(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2); struct ListNode* mergeSort(struct ListNode** lists, int low, int high); struct ListNode* mergeKLists(struct ListNode** lists, int listsSize) { if (!lists || listsSize == 0 ) return NULL; return mergeSort(lists, 0 , listsSize - 1 ); } struct ListNode* mergeSort(struct ListNode** lists, int low, int high) { if (low >= high) { return lists[low]; } int mid = (low + high) / 2 ; struct ListNode* l1 = mergeSort(lists, low, mid); struct ListNode* l2 = mergeSort(lists, mid + 1 , high); return merge(l1, l2); } struct ListNode* merge(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2) { struct ListNode* dum = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); dum->next = NULL; struct ListNode* p = dum; while (l1 && l2) { if (l1->val < l2->val) { p->next = l1; l1 = l1->next; } else { p->next = l2; l2 = l2->next; } p = p->next; } p->next = l1 ? l1 : l2; return dum->next; }
思路2:利用java的小根堆,把所有节点插入到小根堆
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution { public ListNode mergeKLists (ListNode[] lists) { PriorityQueue<ListNode> q = new PriorityQueue <>((a, b) -> a.val - b.val); for (ListNode list : lists) { while (list != null ) { q.add(list); list = list.next; } } ListNode head = new ListNode (); head.next = null ; ListNode r = head; while (!q.isEmpty()) { ListNode node = q.poll(); node.next = r.next; r.next = node; r = node; } return head.next; } }
LRU 缓存 思路:也是非常恶心的题目:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 class LRUCache { class Node { int key; int value; Node pre; Node next; public Node (int key, int value) { this .key = key; this .value = value; } } private HashMap<Integer, Node> map; private Node head; private Node tail; private int capacity; public LRUCache (int capacity) { this .capacity = capacity; map = new HashMap <>(); head = new Node (-1 , -1 ); tail = new Node (-1 , -1 ); head.next = tail; tail.pre = head; } public int get (int key) { Node p = map.get(key); if (p == null ) { return -1 ; } movetofirst(p); return p.value; } public void put (int key, int value) { Node p = map.get(key); if (p == null ) { Node newnode = new Node (key, value); if (map.size() >= capacity) { Node q = deleteTail(); map.remove(q.key); } map.put(key, newnode); addtoHead(newnode); } else { p.value = value; map.put(key, p); movetofirst(p); } } public void addtoHead (Node node) { node.next = head.next; node.pre = head; head.next = node; head.next.next.pre = node; } public void delete (Node node) { node.pre.next = node.next; node.next.pre = node.pre; } public void movetofirst (Node node) { delete(node); addtoHead(node); } public Node deleteTail () { Node p = tail.pre; delete(tail.pre); return p; } }
二叉树 二叉树的中序遍历 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 void zhongxu (struct TreeNode* root, int * res, int * returnSize) ;int * inorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int * returnSize) { int * res = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int ) * 1000 ); *returnSize = 0 ; zhongxu(root, res, returnSize); return res; } void zhongxu (struct TreeNode* root, int * res, int * returnSize) { if (root == NULL) { return ; } zhongxu(root->left, res, returnSize); res[(*returnSize)++] = root->val; zhongxu(root->right, res, returnSize); }
二叉树的最近公共祖先 给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科 中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个节点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个节点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先 )。”
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1 输出:3 解释:节点 5 和节点 1 的最近公共祖先是节点 3 。
思路:对于当前节点root:
如果root为空,返回null
如果root就是p或q,返回root
递归搜索左子树,得到left结果
递归搜索右子树,得到right结果
根据left和right的结果判断:
如果left和right都不为空,说明p和q分别在左右子树,root就是LCA
如果只有left不为空,说明p和q都在左子树,返回left
如果只有right不为空,说明p和q都在右子树,返回right
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 struct TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor (struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q) { if (root == NULL ) return NULL ; if (root == p || root == q) return root; struct TreeNode * left = struct TreeNode * right = if (left != NULL && right != NULL ) { return root; } if (left) { return left; } return right; }
图论 岛屿数量 给你一个由 '1'(陆地)和 '0'(水)组成的的二维网格,请你计算网格中岛屿的数量。
岛屿总是被水包围,并且每座岛屿只能由水平方向和/或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成。
此外,你可以假设该网格的四条边均被水包围。
示例 1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 输入:grid = [ ["1","1","1","1","0"], ["1","1","0","1","0"], ["1","1","0","0","0"], ["0","0","0","0","0"] ] 输出:1
思路:当我们找到一个’1’时,我们从这个位置开始”探索”:
把当前位置标记为已访问(避免重复计算)
递归地访问它的上下左右四个相邻位置
如果相邻位置也是’1’且未被访问过,继续探索
直到把整个岛屿都探索完
算法步骤:
遍历整个网格
当遇到一个’1’且未被访问过时:
岛屿数量+1
从这个位置开始DFS,把整个岛屿都标记为已访问
继续遍历剩余位置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution { public int numIslands (char [][] grid) { int nums = 0 ; boolean [][] visited = new boolean [grid.length][grid[0 ].length]; int row = grid.length; int col = grid[0 ].length; for (int i = 0 ; i < row; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < col; j++) { if (grid[i][j] == '1' && visited[i][j] == false ) { nums++; dfs(grid, i, j, visited); } } } return nums; } public void dfs (char [][] grid, int row, int col, boolean [][] visited) { if (row < 0 || row >= grid.length) return ; if (col < 0 || col >= grid[0 ].length) return ; if (grid[row][col] != '1' || visited[row][col] == true ) return ; visited[row][col] = true ; dfs(grid, row - 1 , col, visited); dfs(grid, row + 1 , col, visited); dfs(grid, row, col + 1 , visited); dfs(grid, row, col - 1 , visited); } }
腐烂的橘子 在给定的 m x n 网格 grid 中,每个单元格可以有以下三个值之一:
值 0 代表空单元格;
值 1 代表新鲜橘子;
值 2 代表腐烂的橘子。
每分钟,腐烂的橘子 周围 4 个方向上相邻 的新鲜橘子都会腐烂。
返回 直到单元格中没有新鲜橘子为止所必须经过的最小分钟数。如果不可能,返回 -1 。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:grid = [[2,1,1],[1,1,0],[0,1,1]] 输出:4
思路:多源BFS(广度优先搜索)同时 、逐层 扩散
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 class Solution { public int orangesRotting (int [][] grid) { int m = grid.length; int n = grid[0 ].length; int freshCount = 0 ; Deque<int []> q = new ArrayDeque <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { if (grid[i][j] == 1 ) { freshCount++; } else if (grid[i][j] == 2 ) { q.add(new int [] { i, j }); } } } boolean hasFulan = false ; int minutes = 0 ; int direction[][] = new int [][] { { -1 , 0 }, { 1 , 0 }, { 0 , -1 }, { 0 , 1 } }; while (!q.isEmpty()) { int size = q.size(); for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) { int lan[] = q.poll(); int row = lan[0 ]; int col = lan[1 ]; for (int j = 0 ; j < direction.length; j++) { int newrow = row + direction[j][0 ]; int newcol = col + direction[j][1 ]; if (newrow < 0 || newrow > grid.length - 1 || newcol < 0 || newcol > grid[0 ].length - 1 ) { continue ; } else { if (grid[newrow][newcol] == 1 ) { hasFulan = true ; grid[newrow][newcol] = 2 ; freshCount--; q.add(new int [] { newrow, newcol }); } } } } if (hasFulan) { minutes++; hasFulan = false ; } } return freshCount == 0 ? minutes : -1 ; } }
课程表 你这个学期必须选修 numCourses 门课程,记为 0 到 numCourses - 1 。
在选修某些课程之前需要一些先修课程。 先修课程按数组 prerequisites 给出,其中 prerequisites[i] = [ai, bi] ,表示如果要学习课程 ai 则 必须 先学习课程 bi 。
例如,先修课程对 [0, 1] 表示:想要学习课程 0 ,你需要先完成课程 1 。
请你判断是否可能完成所有课程的学习?如果可以,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:numCourses = 2, prerequisites = [[1,0]] 输出:true 解释:总共有 2 门课程。学习课程 1 之前,你需要完成课程 0 。这是可能的。
思路1:拓扑排序。构建邻接表和节点的度数组。用一个队列来装入队为0的节点。出队时顺便把邻居的度减一。
思路2:直接用DFS判断是否存在环路。(还没实现)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution { public boolean canFinish (int numCourses, int [][] prerequisites) { List<List<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList <>(); int du[] = new int [numCourses]; for (int i = 0 ; i < numCourses; i++) { graph.add(new ArrayList <>()); } for (int [] data : prerequisites) { int a = data[0 ]; int b = data[1 ]; graph.get(b).add(a); du[a]++; } Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList <>(); int count = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < numCourses; i++) { if (du[i] == 0 ) { q.add(i); } } while (!q.isEmpty()) { int p = q.poll(); count++; List<Integer> list = graph.get(p); for (int i : list) { du[i]--; if (du[i] == 0 ) { q.add(i); } } } if (count == numCourses) { return true ; } return false ; } }
实现 Trie (前缀树) **Trie **(发音类似 “try”)或者说 前缀树 是一种树形数据结构,用于高效地存储和检索字符串数据集中的键。这一数据结构有相当多的应用情景,例如自动补全和拼写检查。
请你实现 Trie 类:
Trie() 初始化前缀树对象。void insert(String word) 向前缀树中插入字符串 word 。boolean search(String word) 如果字符串 word 在前缀树中,返回 true(即,在检索之前已经插入);否则,返回 false 。boolean startsWith(String prefix) 如果之前已经插入的字符串 word 的前缀之一为 prefix ,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 输入 ["Trie", "insert", "search", "search", "startsWith", "insert", "search"] [[], ["apple"], ["apple"], ["app"], ["app"], ["app"], ["app"]] 输出 [null, null, true, false, true, null, true]
思路:把一般的二叉树的左右孩子扩展为一个数组。每个节点都是一个数组。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 class Trie { private Trie[] children; private boolean isEnd; public Trie () { children = new Trie [26 ]; isEnd = false ; } public void insert (String word) { Trie node = this ; for (char i : word.toCharArray()) { int index = i - 'a' ; if (node.children[index] == null ) { node.children[index] = new Trie (); } node = node.children[index]; } node.isEnd = true ; } public Trie searchPrefix (String word) { Trie node = this ; for (char i : word.toCharArray()) { int index = i - 'a' ; if (node.children[index] == null ) { return null ; } node = node.children[index]; } return node; } public boolean search (String word) { return (searchPrefix(word) != null ) && searchPrefix(word).isEnd; } public boolean startsWith (String prefix) { return searchPrefix(prefix) != null ; } }
回溯 全排列 给定一个不含重复数字的数组 nums ,返回其 所有可能的全排列 。你可以 按任意顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:nums = [1,2,3] 输出:[[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
解题思路:回溯算法
全排列问题的核心思想是回溯 ,我们可以把这个过程想象成:
从数组中选择一个数字放在第一位
从剩余数字中选择一个放在第二位
继续这个过程直到所有位置都填满
如果当前路径不满足条件,就回退到上一步,尝试其他选择
具体点:
通过交换元素位置来生成排列
每次将待排列的元素与当前位置index交换
递归处理后续位置
回溯时再次交换回来
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> permute (int [] nums) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); huisu(nums, 0 , res); return res; } public void huisu (int [] nums, int index, List<List<Integer>> res) { if (index == nums.length) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList <>(); for (int num : nums) { list.add(num); } res.add(list); return ; } for (int i = index; i < nums.length; i++) { swap(nums, index, i); huisu(nums, index + 1 , res); swap(nums, index, i); } } public void swap (int nums[], int i, int j) { int temp = nums[j]; nums[j] = nums[i]; nums[i] = temp; } }
子集 给定一个不含重复数字的数组 nums ,返回其 所有可能的全排列 。你可以 按任意顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:nums = [1,2,3] 输出:[[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
思路1:二进制。长度为n的数组子集个数的2ⁿ, 每个元素有两种状态:选择(1) 或不选择(0),这正好对应二进制!
对于数组 [1, 2, 3]:
二进制 000 → 都不选 → []
二进制 001 → 选第0个 → [1]
二进制 010 → 选第1个 → [2]
二进制 011 → 选第0,1个 → [1, 2]
二进制 100 → 选第2个 → [3]
二进制 101 → 选第0,2个 → [1, 3]
二进制 110 → 选第1,2个 → [2, 3]
二进制 111 → 都选 → [1, 2, 3]
总结:
n个元素有2ⁿ个子集
用0到2ⁿ-1的所有整数来表示,即1<<n,for (int i = 0; i < (1 << n); i++)
然后判断这些整数的每一位是否是1,如果是1则加到list里面去;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> subsets (int [] nums) { int n = nums.length; int count = 1 << n; List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < count; i++) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList <>(); for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { if (((i >> j) & 1 ) == 1 ) { list.add(nums[n - j - 1 ]); } } res.add(list); } return res; } }
思路2:迭代法,核心思想:逐个添加元素。
关键洞察: 每次添加一个新元素时,新的子集 = 原有的所有子集 + 原有的所有子集都加上新元素。
初始状态:
第1步:添加元素1
1 2 3 4 5 当前result = [[]] 对每个已有子集,生成包含1的新版本: [] → [] + [1] result = [[], [1]]
第2步:添加元素2
1 2 3 4 5 6 当前result = [[], [1]] 对每个已有子集,生成包含2的新版本: [] → [] + [2] [1] → [1] + [1,2] result = [[], [1], [2], [1,2]]
第3步:添加元素3
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 当前result = [[], [1], [2], [1,2]] 对每个已有子集,生成包含3的新版本: [] → [] + [3] [1] → [1] + [1,3] [2] → [2] + [2,3] [1,2] → [1,2] + [1,2,3] 最终result = [[], [1], [2], [1,2], [3], [1,3], [2,3], [1,2,3]]
每一步的子集数量都会复制一倍:1 → 2 → 4 → 8
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> subsets (int [] nums) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); int n = nums.length; List<Integer> cur = new ArrayList <>(); res.add(cur); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { int size = res.size(); for (int j = 0 ; j < size; j++) { List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList <>(res.get(j)); temp.add(nums[i]); res.add(temp); } } return res; } }
思路3:递归回溯。每一个元素都有两个选择,我要这个元素、我不要这个元素。
核心思想: 对于每个元素,我们都有两个选择:
选择 这个元素加入当前子集不选择 这个元素
具体过程:
从第一个元素开始
对每个元素做决定:要它还是不要它
每做一次决定,就递归处理下一个元素
当处理完所有元素时,得到一个完整的子集
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> subsets (int [] nums) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); List<Integer> cur = new ArrayList <>(); huisu(res, cur, 0 , nums); return res; } public void huisu (List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> cur, int index, int [] nums) { if (index == nums.length) { res.add(new ArrayList <>(cur)); return ; } huisu(res, cur, index + 1 , nums); cur.add(nums[index]); huisu(res, cur, index + 1 , nums); cur.remove(cur.size() - 1 ); } }
电话号码的字母组合 给定一个仅包含数字 2-9 的字符串,返回所有它能表示的字母组合。答案可以按 任意顺序 返回。
给出数字到字母的映射如下(与电话按键相同)。注意 1 不对应任何字母。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:digits = "23" 输出:["ad","ae","af","bd","be","bf","cd","ce","cf"]
核心思想 :使用队列按层处理,每处理一个数字就生成一层新的组合。
具体步骤 (以 digits = "23" 为例):
初始化
:创建一个队列,放入空字符串
处理第一个数字 ‘2’
:
出队空字符串 ""
将 ‘2’ 对应的每个字母(’a’, ‘b’, ‘c’)分别加到空字符串后面
新组合 "a", "b", "c" 依次入队
队列状态:["a", "b", "c"]
处理第二个数字 ‘3’
:
出队 "a",加上 ‘3’ 对应的字母(’d’, ‘e’, ‘f’),得到 "ad", "ae", "af" 入队 队列状态:["b", "c", "ad", "ae", "af"]
出队 "b",加上 ‘3’ 对应的字母,得到 "bd", "be", "bf" 入队["c", "ad", "ae", "af", "bd", "be", "bf"]
出队 "c",加上 ‘3’ 对应的字母,得到 "cd", "ce", "cf" 入队 队列状态:["ad", "ae", "af", "bd", "be", "bf", "cd", "ce", "cf"]
结束 :所有数字处理完毕,队列中的元素就是所有可能的字母组合。
关键点 :每处理一个数字,就要把当前队列中的所有元素都出队一遍,然后生成新的组合入队。这样可以确保每一层的组合都能与下一个数字的所有字母结合。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public List<String> letterCombinations (String digits) { if (digits.length() == 0 ) { return new ArrayList <>(); } Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList <>(); queue.add("" ); String map[] = { "" , "" , "abc" , "def" , "ghi" , "jkl" , "mno" , "pqrs" , "tuv" , "wxyz" }; for (int i = 0 ; i < digits.length(); i++) { int index = digits.charAt(i) - '0' ; String str = map[index]; int n = queue.size(); for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { String temp = queue.poll(); for (char ch : str.toCharArray()) { queue.add(temp + ch); } } } return new ArrayList <>(queue); } }
组合总和 给你一个 无重复元素 的整数数组 candidates 和一个目标整数 target ,找出 candidates 中可以使数字和为目标数 target 的 所有 不同组合 ,并以列表形式返回。你可以按 任意顺序 返回这些组合。
candidates 中的 同一个 数字可以 无限制重复被选取 。如果至少一个数字的被选数量不同,则两种组合是不同的。
对于给定的输入,保证和为 target 的不同组合数少于 150 个。
示例 1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 输入:candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7 输出:[[2,2,3],[7]] 解释: 2 和 3 可以形成一组候选,2 + 2 + 3 = 7 。注意 2 可以使用多次。 7 也是一个候选, 7 = 7 。 仅有这两种组合。
关键步骤总结
检查答案 :if (sum == target) - 凑够了就是答案检查超限 :if (sum > target) - 加多了就退出做选择 :current.add(candidates[i]) - 放进篮子递归 :backtrack(..., i, ...) - 继续凑,可以重复选撤销 :current.remove(...) - 拿出来,试试别的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum (int [] candidates, int target) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); List<Integer> cur = new ArrayList <>(); huisu(candidates, res, cur, 0 , target, 0 ); return res; } public void huisu (int [] candidates, List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> cur, int index, int target, int sum) { if (sum == target) { res.add(new ArrayList <>(cur)); return ; } if (sum > target) { return ; } for (int i = index; i < candidates.length; i++) { cur.add(candidates[i]); huisu(candidates, res, cur, i, target, sum + candidates[i]); cur.remove(cur.size() - 1 ); } } }
括号生成 数字 n 代表生成括号的对数,请你设计一个函数,用于能够生成所有可能的并且 有效的 括号组合。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:n = 3 输出:["((()))","(()())","(())()","()(())","()()()"]
解题思路 两段回溯
有效括号的规则 :
左括号数量 = 右括号数量 = n
在任意位置,左括号数量 ≥ 右括号数量 (不能出现)(这种情况)
左括号剪枝 :if (left< n) - 左括号不能超过n个
右括号剪枝 :if (right< lef) - 右括号不能超过左括号
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution { public List<String> generateParenthesis (int n) { List<String> res = new ArrayList <>(); List<Character> cur = new ArrayList <>(); huisu(n, cur, res, 0 , 0 ); return res; } public void huisu (int n, List<Character> cur, List<String> res, int left, int right) { if (cur.size() == n * 2 ) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); for (char ch : cur) { sb.append(ch); } res.add(sb.toString()); return ; } if (left < n) { cur.add('(' ); huisu(n, cur, res, left + 1 , right); cur.remove(cur.size() - 1 ); } if (right < left) { cur.add(')' ); huisu(n, cur, res, left, right + 1 ); cur.remove(cur.size() - 1 ); } } }
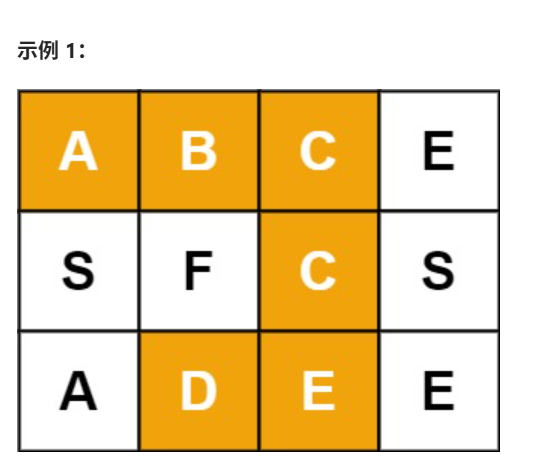
单词搜索
1 2 输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCCED" 输出:true
解法:
这是一个典型的二维网格回溯 问题:
遍历每个起点 :找到单词第一个字母的位置作为起点四方向搜索 :从起点向上下左右四个方向搜索下一个字母标记访问状态 :提前保持好字母,然后用#标记数组避免重复使用同一个格子回溯 :如果当前路径不行,撤销标记#,尝试其他路径
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 class Solution { public boolean exist (char [][] board, String word) { int m = board.length; int n = board[0 ].length; for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { if (huisu(board, i, j, word, 0 , m, n)) { return true ; } } } return false ; } public boolean huisu (char [][] board, int i, int j, String word, int index, int m, int n) { if (index == word.length()) { return true ; } if (i < 0 || i > m - 1 || j < 0 || j > n - 1 || board[i][j] != word.charAt(index)) { return false ; } char temp = board[i][j]; board[i][j] = '#' ; boolean isTrue = huisu(board, i + 1 , j, word, index + 1 , m, n) || huisu(board, i - 1 , j, word, index + 1 , m, n) || huisu(board, i, j + 1 , word, index + 1 , m, n) || huisu(board, i, j - 1 , word, index + 1 , m, n); if (isTrue == true ) { return true ; } board[i][j] = temp; return false ; } }
分割回文串 给你一个字符串 s,请你将 s 分割成一些 子串,使每个子串都是 回文串 。返回 s 所有可能的分割方案。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:s = "aab" 输出:[["a","a","b"],["aa","b"]]
解法:
基本流程 :
选择分割点 :在每个位置尝试分割字符串验证回文 :检查分割出的子串是否为回文递归继续 :如果是回文,继续分割剩余字符串回溯尝试 :如果当前分割不行,撤销选择,尝试其他分割点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 class Solution { public List<List<String>> partition (String s) { List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList <>(); List<String> cur = new ArrayList <>(); huisu(res, s, cur, 0 ); return res; } public void huisu (List<List<String>> res, String s, List<String> cur, int index) { if (index == s.length()) { res.add(new ArrayList <>(cur)); return ; } for (int i = index; i < s.length(); i++) { String str = s.substring(index, i + 1 ); if (isHui(str)) { cur.add(str); huisu(res, s, cur, i + 1 ); cur.remove(cur.size() - 1 ); } } } public boolean isHui (String s) { int i = 0 ; int j = s.length() - 1 ; while (i < j) { if (s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)) { return false ; } i++; j--; } return true ; } }
栈 最小栈 设计一个支持 push ,pop ,top 操作,并能在常数时间内检索到最小元素的栈。
实现 MinStack 类:
MinStack() 初始化堆栈对象。void push(int val) 将元素val推入堆栈。void pop() 删除堆栈顶部的元素。int top() 获取堆栈顶部的元素。int getMin() 获取堆栈中的最小元素。
解题思路 核心思想:辅助栈法
关键在于如何在O(1)时间复杂度内获取最小值。我们使用两个栈来解决这个问题:
**主栈 (stack)**:存储所有元素,维护正常的栈操作
**辅助栈 (fuzhu)**:专门维护当前栈中的最小值信息
辅助栈的维护策略:
入栈时 :只有当新元素小于等于辅助栈顶元素时,才将其推入辅助栈出栈时 :只有当主栈出栈元素等于辅助栈顶元素时,辅助栈才同步出栈
这样设计的优势是辅助栈的栈顶始终保存着当前主栈中的最小值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class MinStack { Stack<Integer> stack; Stack<Integer> fuzhu; public MinStack () { stack = new Stack <>(); fuzhu = new Stack <>(); } public void push (int val) { stack.push(val); if (fuzhu.isEmpty() || val <= fuzhu.peek()) { fuzhu.push(val); } } public void pop () { int removedElement = stack.pop(); if (removedElement == fuzhu.peek()) { fuzhu.pop(); } } public int top () { return stack.peek(); } public int getMin () { return fuzhu.peek(); } }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度 :所有操作均为 O(1)空间复杂度 :O(n),最坏情况下辅助栈需要存储所有元素
字符串解码 给定一个经过编码的字符串,返回它解码后的字符串。
编码规则为: k[encoded_string],表示其中方括号内部的 encoded_string 正好重复 k 次。注意 k 保证为正整数。
你可以认为输入字符串总是有效的;输入字符串中没有额外的空格,且输入的方括号总是符合格式要求的。
此外,你可以认为原始数据不包含数字,所有的数字只表示重复的次数 k ,例如不会出现像 3a 或 2[4] 的输入。
示例 1:
1 2 输入:s = "3[a]2[bc]" 输出:"aaabcbc"
示例 2:
1 2 输入:s = "3[a2[c]]" 输出:"accaccacc"
核心思想:双栈法处理嵌套结构
这是一个典型的嵌套结构解析问题,使用栈来处理递归结构是最自然的选择。
算法设计 :
**数字栈 (numStack)**:存储重复次数 k
**字符串栈 (strStack)**:存储当前层级之前的字符串
**当前数字 (currNum)**:累积正在读取的数字
**当前字符串 (currStr)**:累积当前层级的字符串
处理逻辑 :
遇到数字:累积到 currNum
遇到 [:将当前状态压栈,重置当前变量
遇到 ]:出栈并构造重复字符串
遇到字母:累积到 currStr
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class Solution { public String decodeString (String s) { Stack<Integer> numStack = new Stack <>(); Stack<String> strStack = new Stack <>(); int currNum = 0 ; String currStr = "" ; for (char ch : s.toCharArray()) { if (Character.isDigit(ch)) { currNum = currNum * 10 + (ch - '0' ); } else if (ch == '[' ) { numStack.push(currNum); strStack.push(currStr); currNum = 0 ; currStr = "" ; } else if (ch == ']' ) { int repeatTimes = numStack.pop(); String previousStr = strStack.pop(); StringBuilder temp = new StringBuilder (); for (int i = 0 ; i < repeatTimes; i++) { temp.append(currStr); } currStr = previousStr + temp.toString(); } else { currStr += ch; } } return currStr; } }
每日温度 给定一个整数数组 temperatures ,表示每天的温度,返回一个数组 answer ,其中 answer[i] 是指对于第 i 天,下一个更高温度出现在几天后。如果气温在这之后都不会升高,请在该位置用 0 来代替。
示例 1:
1 2 输入: temperatures = [73,74,75,71,69,72,76,73] 输出: [1,1,4,2,1,1,0,0]
思路:利用单调栈,栈里记录的是下标,如果当前值比栈顶元素大,说明栈顶元素找到了下一个更高气温,用一个结果数组记录后弹出栈,直到栈空或当前温度不再更大,再入栈。如果当前值比栈顶元素小,直接入栈。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int [] dailyTemperatures(int [] temperatures) { Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack <>(); int [] result = new int [temperatures.length]; for (int i = 0 ; i < temperatures.length; i++) { while (!stack.isEmpty() && temperatures[i] > temperatures[stack.peek()]) { int prevIndex = stack.pop(); result[prevIndex] = i - prevIndex; } stack.push(i); } return result; } }
堆 数组中的第K个最大元素 给定整数数组 nums 和整数 k,请返回数组中第 **k** 个最大的元素。
请注意,你需要找的是数组排序后的第 k 个最大的元素,而不是第 k 个不同的元素。
你必须设计并实现时间复杂度为 O(n) 的算法解决此问题。
示例 1:
1 2 输入: [3,2,1,5,6,4], k = 2 输出: 5
思路1:基于快速排序的分治思想,但只需要处理包含第k大元素的那一部分。划分一次后会固定一个元素的位置,且该元素左边都比它小,右边都比它大。如果当前元素下标<n-k,说明第 k 个最大的元素在右边,否则在左边。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { public int findKthLargest (int [] nums, int k) { return quickSelect(nums, k, 0 , nums.length - 1 ); } private int quickSelect (int [] nums, int k, int left, int right) { int pivotIndex = partition(nums, left, right); int targetIndex = nums.length - k; if (pivotIndex == targetIndex) { return nums[pivotIndex]; } else if (pivotIndex > targetIndex) { return quickSelect(nums, k, left, pivotIndex - 1 ); } else { return quickSelect(nums, k, pivotIndex + 1 , right); } } private int partition (int [] nums, int left, int right) { int pivot = nums[left]; while (left < right) { while (left < right && nums[right] >= pivot) right--; nums[left] = nums[right]; while (left < right && nums[left] <= pivot) left++; nums[right] = nums[left]; } nums[left] = pivot; return left; } }
思路2:堆排序法,建立大根堆,建立好之后,每选择一次堆顶元素后调整大根堆,要找第 k 个最大的元素,则选择k-1次调整k-1次。最后的堆顶元素就是第 k 个最大的元素
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public int findKthLargest (int [] arr, int k) { build(arr); for (int j = arr.length - 1 ; j >= arr.length - 1 - k + 2 ; j--) { int teem = arr[0 ]; arr[0 ] = arr[j]; arr[j] = teem; adjust(arr, 0 , j - 1 ); } return arr[0 ]; } public static void build (int [] arr) { for (int i = (arr.length - 1 ) / 2 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { adjust(arr, i, arr.length - 1 ); } } public static void adjust (int [] arr, int k, int n) { for (int i = k * 2 + 1 ; i <= n; i = i * 2 + 1 ) { if (i < n && arr[i] < arr[i + 1 ]) { i++; } if (arr[k] < arr[i]) { int temp = arr[k]; arr[k] = arr[i]; arr[i] = temp; k = i; } } }
思路3:小根堆法,只维护一个大小为k的小根堆,如果堆的大小超过k时,移除堆顶(最小)元素,最终堆顶元素就是第 k 个最大的元素。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public int findKthLargest (int [] nums, int k) { PriorityQueue<Integer> minHeap = new PriorityQueue <>(); for (int num : nums) { minHeap.add(num); if (minHeap.size() > k) { minHeap.poll(); } } return minHeap.peek(); }
思路4:桶排序,将数组的数据放在若干个桶中,桶中记录的是相同元素的个数,桶的下标代表值(但不是真实值),倒着遍历桶,如果个数超过了k,说明第 k 个最大的元素就在这个桶中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public int findKthLargest (int [] arr, int k) { int max = arr[0 ]; int min = arr[0 ]; for (int i : arr) { max = Math.max(max, i); min = Math.min(min, i); } int range = max - min + 1 ; int tong[] = new int [range]; for (int i = 0 ; i < arr.length; i++) { tong[arr[i] - min]++; } int count = 0 ; for (int j = range - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j--) { count = count + tong[j]; if (count >= k) return j + min; } return 0 ; }
前 K 个高频元素 给你一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数 k ,请你返回其中出现频率前 k 高的元素。你可以按 任意顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
1 2 输入: nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2 输出: [1,2]
思路1:小根堆。维护一个大小为k的小根堆。遍历玩数组后小根堆里剩下的出现频率前 k 高的元素。因为没当小根堆的大小大于k时,堆顶元素就被移除,移除的是最小值。所以剩下的就是最大值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public int [] topKFrequent(int [] nums, int k) { Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); for (int num : nums) { map.put(num, map.getOrDefault(num, 0 ) + 1 ); } PriorityQueue<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>> dui = new PriorityQueue <>( (a, b) -> a.getValue() - b.getValue() ); for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) { dui.add(entry); if (dui.size() > k) { dui.poll(); } } int res[] = new int [k]; for (int i = 0 ; i < k; i++) { res[i] = dui.poll().getKey(); } return res; }
思路2:桶排序,将频率作为桶的索引,频率最小值为1,所以桶的大小为nums.length + 1。桶里存放频率对应的数据。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public int [] topKFrequent(int [] nums, int k) { Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); for (int num : nums) { map.put(num, map.getOrDefault(num, 0 ) + 1 ); } ArrayList<Integer> tong[] = new ArrayList [nums.length + 1 ]; for (Map.Entry entry : map.entrySet()) { int key = (int ) entry.getKey(); int value = (int ) entry.getValue(); if (tong[value] == null ) { tong[value] = new ArrayList <>(); } tong[value].add(key); } int count = 0 ; int res[] = new int [k]; for (int j = tong.length - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j--) { if (tong[j] != null ) for (int v : tong[j]) { res[count++] = v; if (count == k) { return res; } } } return res; }
贪心算法 买卖股票的最佳时机 给定一个数组 prices ,它的第 i 个元素 prices[i] 表示一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。
你只能选择 某一天 买入这只股票,并选择在 未来的某一个不同的日子 卖出该股票。设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。
返回你可以从这笔交易中获取的最大利润。如果你不能获取任何利润,返回 0 。
示例 1:
1 2 3 4 输入:[7,1,5,3,6,4] 输出:5 解释:在第 2 天(股票价格 = 1)的时候买入,在第 5 天(股票价格 = 6)的时候卖出,最大利润 = 6-1 = 5 。 注意利润不能是 7-1 = 6, 因为卖出价格需要大于买入价格;同时,你不能在买入前卖出股票。
思路:没什么好说的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { int min=100000 ; int profit=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<prices.length;i++){ min=Math.min(min,prices[i]); profit=Math.max(profit,prices[i]-min); } return profit; }
跳跃游戏 给你一个非负整数数组 nums ,你最初位于数组的 第一个下标 。数组中的每个元素代表你在该位置可以跳跃的最大长度。
判断你是否能够到达最后一个下标,如果可以,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
1 2 3 输入:nums = [2,3,1,1,4] 输出:true 解释:可以先跳 1 步,从下标 0 到达下标 1, 然后再从下标 1 跳 3 步到达最后一个下标。
思路:没什么好说的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class Solution { public boolean canJump (int [] nums) { int maxlengthIndex=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<nums.length;i++){ if (i>maxlengthIndex) return false ; maxlengthIndex=Math.max(maxlengthIndex,i+nums[i]); } return true ; } }
跳跃游戏2 给定一个长度为 n 的 0 索引 整数数组 nums。初始位置为 nums[0]。
每个元素 nums[i] 表示从索引 i 向后跳转的最大长度。换句话说,如果你在 nums[i] 处,你可以跳转到任意 nums[i + j] 处:
0 <= j <= nums[i]i + j < n
返回到达 nums[n - 1] 的最小跳跃次数。生成的测试用例可以到达 nums[n - 1]。
示例 1:
1 2 3 4 输入: nums = [2,3,1,1,4] 输出: 2 解释: 跳到最后一个位置的最小跳跃数是 2。 从下标为 0 跳到下标为 1 的位置,跳 1 步,然后跳 3 步到达数组的最后一个位置。
思路:贪心算法的都不会,只知道怎么写。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public int jump (int [] nums) { int curr = 0 ; int max = 0 ; int count = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length - 1 ; i++) { max = Math.max(max, nums[i] + i); if (i == curr) { count++; curr = max; } } return count; } }
划分字母区间 给你一个字符串 s 。我们要把这个字符串划分为尽可能多的片段,同一字母最多出现在一个片段中。例如,字符串 "ababcc" 能够被分为 ["abab", "cc"],但类似 ["aba", "bcc"] 或 ["ab", "ab", "cc"] 的划分是非法的。
注意,划分结果需要满足:将所有划分结果按顺序连接,得到的字符串仍然是 s 。
返回一个表示每个字符串片段的长度的列表。
示例 1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 输入:s = "ababcbacadefegdehijhklij" 输出:[9,7,8] 解释: 划分结果为 "ababcbaca"、"defegde"、"hijhklij" 。 每个字母最多出现在一个片段中。 像 "ababcbacadefegde", "hijhklij" 这样的划分是错误的,因为划分的片段数较少。
思路:不会,贪心算法的都不会,只知道怎么写。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public List<Integer> partitionLabels (String s) { int zimu[] = new int [26 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) { zimu[s.charAt(i) - 'a' ] = i; } List<Integer> List = new ArrayList <>(); int max = 0 ; int start = 0 ; int end = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) { max = Math.max(max, zimu[s.charAt(i) - 'a' ]); if (i == max) { List.add(i + 1 - start); start = i + 1 ; } } return List; } }